Spin spirals
Generalized Bloch condition
Spin spirals may be conveniently modeled using a generalization of the Bloch condition (set LNONCOLLINEAR=.TRUE. and LSPIRAL=.TRUE.):
i.e., from one unit cell to the next the up- and down-spinors pick up an additional phase factor of and , respectively, where R is a lattice vector of the crystalline lattice, and q is the so-called spin-spiral propagation vector.
The spin-spiral propagation vector is commonly chosen to lie within the first Brillouin zone of the reciprocal space lattice, and has to be specified by means of the QSPIRAL-tag.
The generalized Bloch condition above gives rise to the following behavior of the magnetization density:
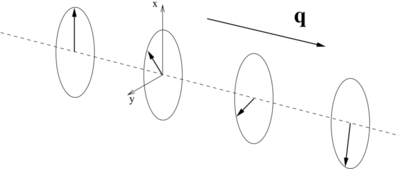
This is schematically depicted below: the components of the magnization in the xy-plane rotate about the spin-spiral propagation vector q.
Basis set considerations
The generalized Bloch condition redefines the Bloch functions as follows:
This changes the Hamiltonian only minimally:
where in and the kinetic energy of a plane wave component changes to:
In the case of spin-spiral calculations the cutoff energy of the basis set of the individual spinor components is specified by means of the ENINI-tag.
Additionally one needs to set ENMAX appropriately: ENMAX needs to be chosen larger than ENINI, and large enough so that the plane wave components of both the up-spinors as well as the components of the down-spinor all have a kinetic energy smaller than ENMAX. This is the case when:
where
In most cases it is more than sufficient to set ENMAX=ENINI+100.
To judge whether ENMAX is chosen large enough one will always get a warning at runtime, e.g.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | | W W AA RRRRR N N II N N GGGG !!! | | W W A A R R NN N II NN N G G !!! | | W W A A R R N N N II N N N G !!! | | W WW W AAAAAA RRRRR N N N II N N N G GGG ! | | WW WW A A R R N NN II N NN G G | | W W A A R R N N II N N GGGG !!! | | | | To represent the spin spiral you requested, with a kinetic | | energy cutoff of ENINI= 300.00 eV, choose ENMAX > 331.21 eV | | Currently ENMAX= 400.00 eV | | | -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Symmetry
Generally the introduction of a spin-spiral will lower the symmetry of the system. At present VASP can not correctly account for the presence of a spin-spiral in its symmetry analysis.
Therefore the use of symmetry has to be switched of completely:
ISYM = -1
Initialisation of the magnetic moments
Related Tags and Sections
LSPIRAL, QSPIRAL, LZEROZ, LNONCOLLINEAR, MAGMOM, ENINI, ENMAX, ISYM, I_CONSTRAINED_M, LAMBDA, M_CONSTR, RWIGS