XANES in Diamond
(UNDER CONSTRUCTION)
Task
Calculation of the XANES K-edge in diamond using the supercell core-hole method.
Input
POSCAR
cubic diamond 3.567 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.5 2 direct 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.25 0.25 0.25
- We will not use this structure as input but rather use it to construct a super cell from it that is actually used in the calculations.
INCAR
System = DIAMOND ALGO = FAST ISMEAR = 0; SIGMA = 0.1; ICORELEVEL = 2 CLNT = 1 CLN = 1 CLL = 0 CLZ = 1.0 CH_LSPEC = .TRUE. CH_SIGMA = 0.5 NBANDS = 300 LREAL = A
- To promote a core electron into the conduction bands and hence create the core-hole ICORELEVEL=2 has to be set. This corresponds to the final state approximation
- CLNT=1 selects the first atom species in the POSCAR file.
- CLN=1 selects main quantum number 1 (hence K-edge).
- CLL=0 selects angular quantum number 0 (s).
- CLZ=1.0 selects the charge of the core hole. By setting this number to a fractional value we can mimick different screening of the electrons. Since this purely exploits error cancellation and the physical background of non-integer charges is not defined well, it should be only used with caution.
- By setting CH_LSPEC=.TRUE. we enable the calculation of matrix elements between core and conduction states and the calculation of the core electron absorption spectrum.
- The broadening of the core electron absorption spectrum is controlled by the tag CH_SIGMA. Usually it is good practice to set this value low and broaden the spectrum in post processing.
- We have to set NBANDS to a larger value to consider enough conduction band states in the calculation.
- Since super cells are used the calculation of the projection operators in real space is much faster, hence LREAL=A is set.
Calculation
Step 1 build a supercell
To perform calculations with a core-hole we need sufficiently large super cells to reduce the interaction of neighbouring core-holes. Usually the obtained spectrum with respect to the size of the super cell has to be converged. This means calculations are done with successively larger cells until no significant change is visible in the spectrum anymore. To save computational time we chose a cell for this tutorial, although for converged values one should use at least .
The super cell can be obtained either by taking the file POSCAR.3x3x3 provided with this tutorial. In the following we show how to get the super cell from the primitive cell using p4vasp:
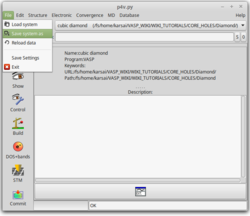
- Open p4vasp by typing p4v on the terminal.
- Load the primitive cell by clicking on File→Load system:
- Multiply cell in each direction (enter 3 for each direction) by clicking on Edit→Multiply Cell:
- Save new system by clicking on File→Save system as:
Step 2 Prepare input files
The first few lines of the POSCAR file for the super cell should look like the following
cubic diamond 3.567 +1.5000000000 +1.5000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +1.5000000000 +1.5000000000 +1.5000000000 +0.0000000000 +1.5000000000 54 Cartesian +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.2500000000 +0.2500000000 +0.2500000000 +0.5000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.5000000000
Here we have only one atom species with 54 atoms (line 6). To construct a core hole on a single atom we have to, take one of these atoms and treat it as a different species. We choose the first atom and we end up with 1 and 53 in the 6th line of the modified POSCAR file
cubic diamond 3.567 +1.5000000000 +1.5000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +1.5000000000 +1.5000000000 +1.5000000000 +0.0000000000 +1.5000000000 1 53 Cartesian +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.2500000000 +0.2500000000 +0.2500000000 +0.5000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.5000000000
Accordingly we have to set CLNT=1 in the INCAR file which selects the first atom species in POSCAR to carry the core-hole.
Download
Back to the main page.